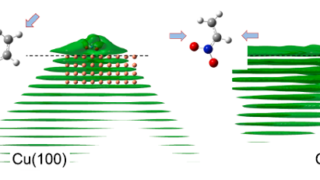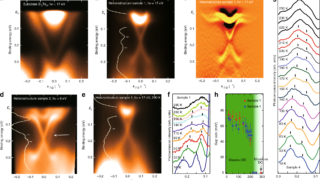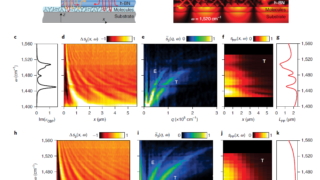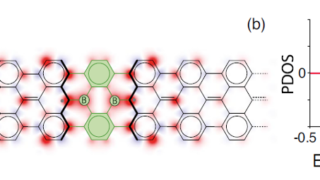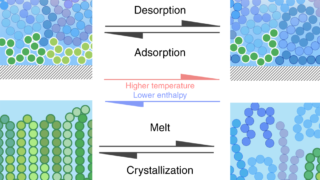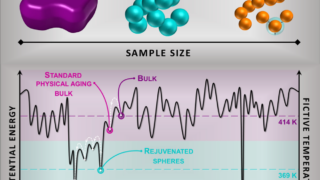
Reaching the ideal glass in polymer spheres
Common glass, used in windows or bottles, for example, is made by heating a mixture of calcium oxide (lime), sodium carbonate (soda), and silicon (IV) oxide (sand), resulting in a calcium silicate. This silicate is not a crystal but a solid in which atoms are random and have no long-range ordered pattern. These kind of […]