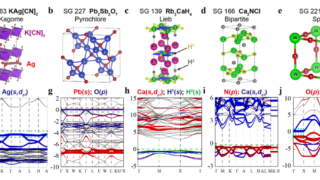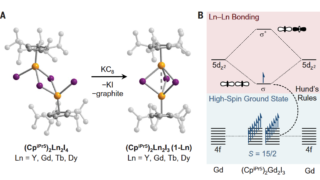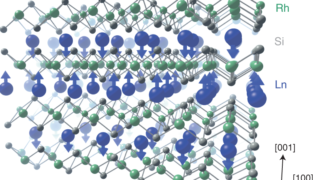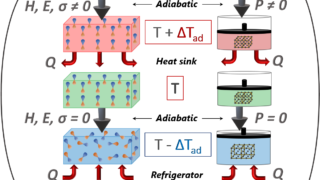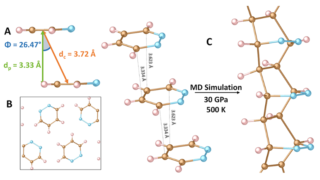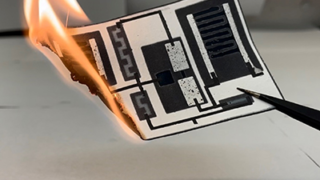
Disposable papertronics
Discarded electronic devices, such as cell phones, are a fast-growing source of waste. One way to mitigate the problem could be to use components that are made with renewable resources and that are easy to dispose of responsibly. Now, researchers have created disposable papertronics, a prototype circuit board that is made of a sheet of […]