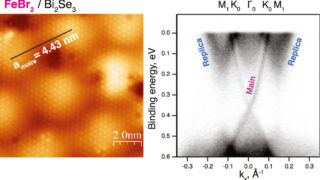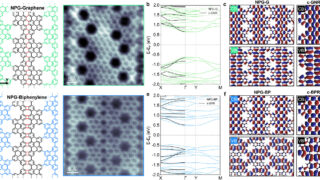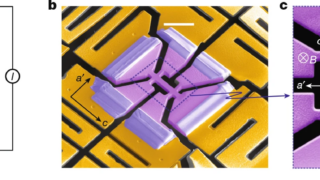
The intertwined nature of electronic waves in 2D TiSe2 crystals
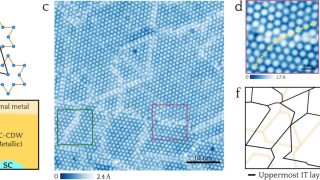
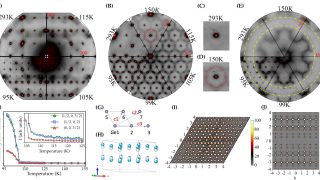
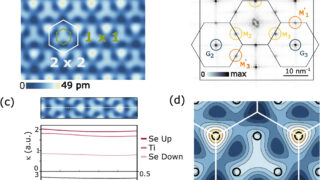
When we peel a crystal down to its very last layer, the physics governing its behavior undergoes a radical shift. This transition from the bulk (three-dimensional) to the two-dimensional limit is where some of the most exotic phenomena in condensed matter physics emerge. Among these, Titanium Diselenide, or TiSe₂, has long fascinated researchers because of […]