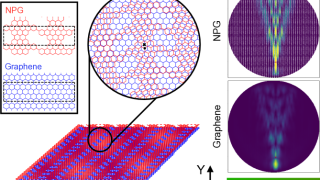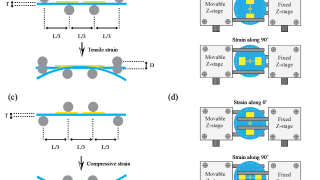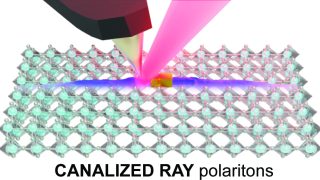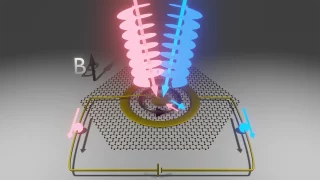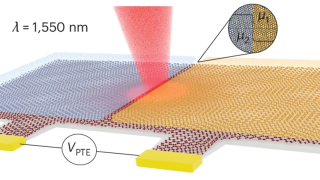
Graphene’s magic twist: fast and slow electrons
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb pattern, is renowned for its ability to conduct electricity with ease. When two graphene sheets are stacked and twisted at a “magic angle” of about one degree, something remarkable happens: the electrons slow down dramatically, creating “flat bands” where they interact strongly. A new […]