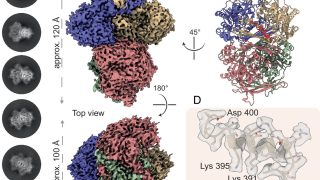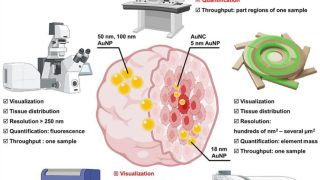
How tiny particles navigate tumours: Understanding nanoparticle penetration in 3D cell models
Biochemistry • DIPC Biochemistry • Materials • Nanotechnology • Pharmacy
Nanoparticles, those minuscule marvels measured in billionths of a metre, hold immense promise for revolutionizing cancer treatment. Their ability to deliver drugs directly to tumours could transform therapies, but only if they can navigate the dense, complex environment of tumour tissue. A new review , that includes a new experimental data set, explores this challenge […]