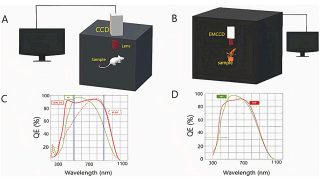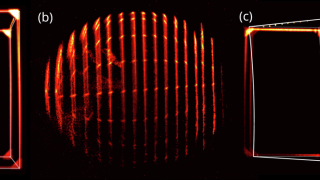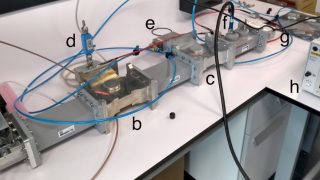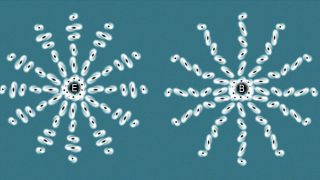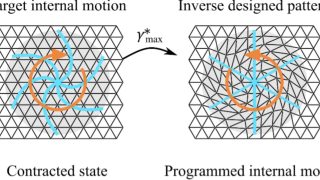
Kirigami, inverse design with no advanced computational tools
Kirigami is a traditional Japanese art form that entails cutting and folding paper (origami is just folding it) to produce complex three-dimensional (3D) structures or objects. Over the past decades, this creative practice has also been applied in the context of physics, engineering, and materials science research to create new materials, devices and even robotic […]