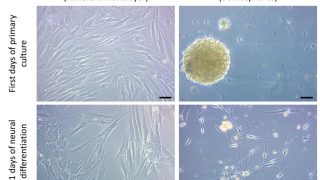
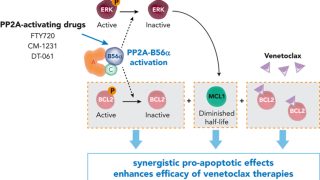
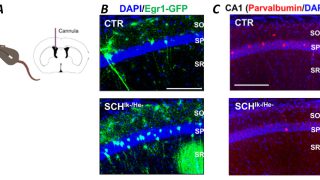
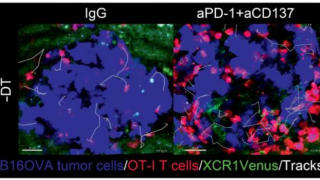
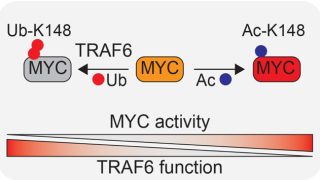
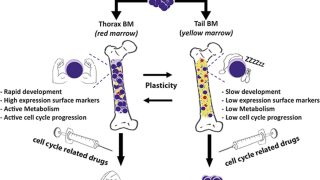
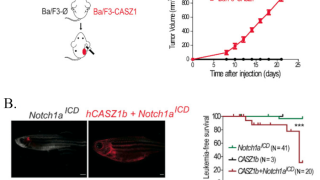
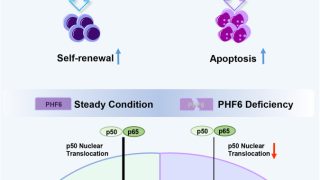
Targeting aberrant DNA methylation in mesenchymal stromal cells as a treatment for myeloma bone disease
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable hematological malignancy characterized by clonal expansion of plasma cells in the bone marrow (BM) . Nearly 90% of myeloma patients suffer from skeletal-related events during the course of the disease that not only affect the quality of life but also their overall survival . Myeloma-associated bone disease (MBD) is […]