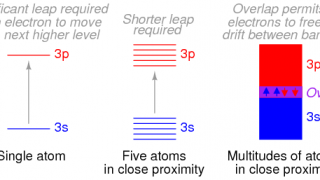
Tuning graphene adsorption continuously
Since the discovery that graphene, the two dimensional carbon allotrope, can be isolated and incorporated into electronic devices intense research efforts have been triggered. Driving forces behind the experimental and theoretical studies of graphene are, e.g., the exceptional electronic properties, in particular the high electron mobilities, the long spin coherence lengths and the possibility to […]