MI weekly selection #150
MI weekly selection #150
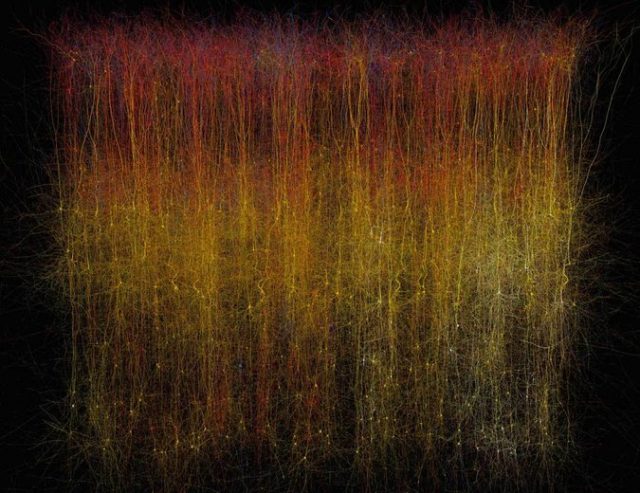
Portion of rat brain reconstructed in computer
A group of 82 neuroscientists have built a portion of a rat’s brain in a computer. The reconstruction is the work of the controversial Blue Brain Project, which hopes to complete a rat brain and move on to a human brain one day. The computerized brain section, culled from various cell data, responded like living tissue when brain activity was simulated.
Evidence that long-lived lakes once existed on Mars found
Mars once had long-lived freshwater lakes within Gale Crater, increasing the chance that life existed there billions of years ago. Researchers poured over photos the rover Curiosity took throughout its journey to Mount Sharp and found lots of evidence of rivers, lakes and deltas.
Genome of 4,500-year-old African man offers clues about migration
DNA from a 4,500-year-old skull found in a cave in Ethiopia is giving scientists clues about migration to and from Africa when compared with modern African DNA. Researchers were able to reconstruct the man’s genome, which revealed that his ancestors had never moved from Africa. When compared with modern African genomes, scientists found that the genetic makeup of Africa changed about 1,500 years after the man’s death.
Gene that suppresses cancer cells abundant in elephants
Elephants have multiple copies of a gene that suppresses cancer cells. Elephants boast 20 copies of the p53 gene, compared with the single copy that exists in humans and other mammals. The gene reacts to DNA damage in cells, either repairing them or killing them off.
A blood test for heart attack risk
Researchers analyzed the blood troponin levels of 6,304 patients and found that a high-sensitivity blood test demonstrated a 99.6% accuracy rate in identifying patients who are less likely to experience heart attack. Low levels of blood troponin were associated with the reduced cardiac event risk.