MI weekly selection #505
MI weekly selection #505
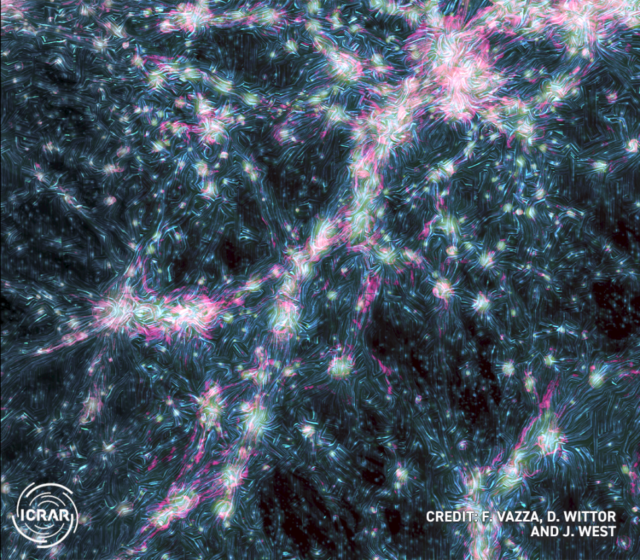
Shockwaves through the “cosmic web” spotted
Astronomers have detected the first evidence of shockwaves in intergalactic magnetic fields running throughout the cosmic web. Researchers combined data from four radio wave detection sites to identify the waves resulting from merging matter in the network of filaments that weave galaxies together.
Full Story: Space
First wiring map of insect’s brain
The first detailed wiring map of an insect’s brain over more than a decade of research has been presented. The fruit fly larva’s brain consists of 3,016 neurons connected by 548,000 synapses and a right and left side, which functions differently than a human brain but can serve as a reference for future neural mapping efforts.
Full Story: National Public Radio
Seismometers can help find fluids under volcanoes
Earthquake wave data captured by 33 seismometers were used to map geothermal fluids under the Bolivian Andes’ Uturuncu volcano. Researchers, who pinpointed fluids based on how crust absorbed energy from 1,356 earthquakes over more than two years, say the technique could help scientists find metals, tap geothermal energy and identify hazards beneath volcanoes.
Full Story: Eos
Bacteria enzyme converts hydrogen to electricity
Scientists have identified an enzyme that allows some bacteria to absorb hydrogen from the air and use it as an energy source. The hydrogenase enzyme can consume tiny amounts of hydrogen even when isolated from the bacteria and convert the element to electricity, which could serve as a potential energy source for small air-powered devices such as a clock or LED globe.
Full Story: The Conversation
Gene that protected from Black Death has a dark side
Some people may have inherited a genetic variant that protected their ancestors from bubonic plague and now protects them from respiratory diseases, including COVID-19 and pneumonia, but that variant is also associated with an elevated risk for autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Researchers analyzed three large genetic studies and found an association between variation in the ERAP2 gene and autoimmune disease and infection risks, and they say the finding may help researchers refine therapeutics for people with certain diseases.
Full Story: HealthDay News