Ultrasensitive molecular sensing with surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA)
Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Quantum physics
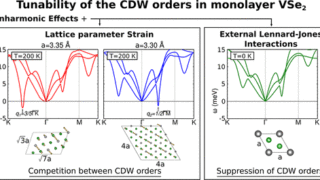
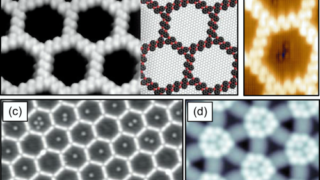
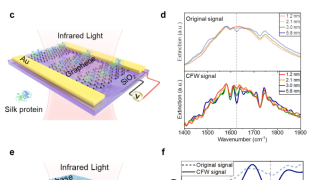
Sensors are essential tools for detecting and analysing trace molecules in a variety of fields, including environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health. However, developing sensors with high enough sensitivity to detect these tiny amounts of molecules remains a challenge. One promising approach is surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), which uses plasmonic nanostructures to amplify the […]