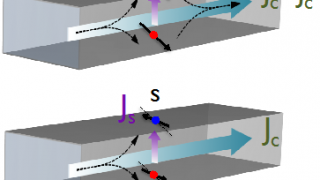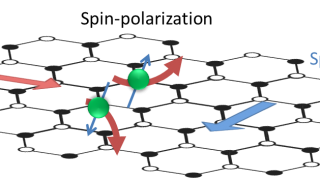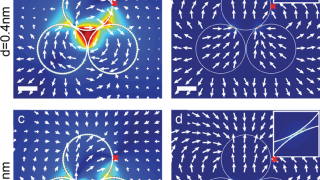
The classical behaviour of the dark modes of silver nanotrimers
Nanoparticles of certain metals, like gold or silver, have attracted substantial interest in recent years owing to their ability to support localized surface plasmon resonances (collective oscillations of conduction electrons). These plasmonic excitations allow manipulation of light at the nanoscale and have enabled technological advances ranging from improved catalytic and photovoltaic cell efficiencies to sensitive […]