Modulation of the resistance of thin metals using the Hanle effect
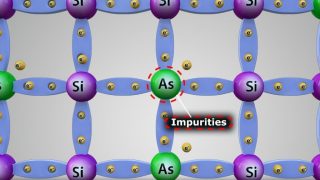
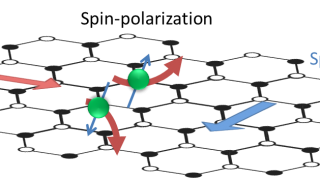
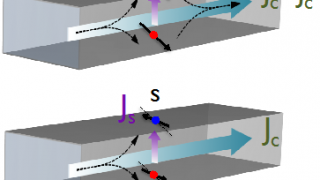
A new vista in spintronics was opened in 2004 with the observation of the spin Hall effect in GeAs at 20 K by David Awschlom and his group. In the spin Hall effect the electrons of a charge current flow in a nonmagnetic conducting material in the absence of an external magnetic field. An applied […]