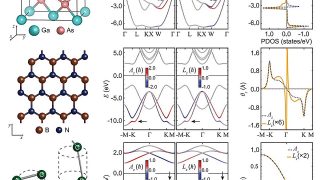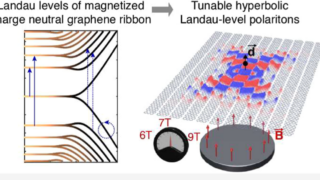
Tunable hyperbolic magnetoexciton polaritons in neutral graphene
Imagine a sheet of material so incredibly thin it’s just one atom thick, yet it can capture and guide light in ways that defy our everyday intuition. This isn’t science fiction—it’s graphene, a wonder material made from carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb pattern. Now, picture slicing this sheet into tiny ribbons, arranging them in […]