MI weekly selection #191
MI weekly selection #191
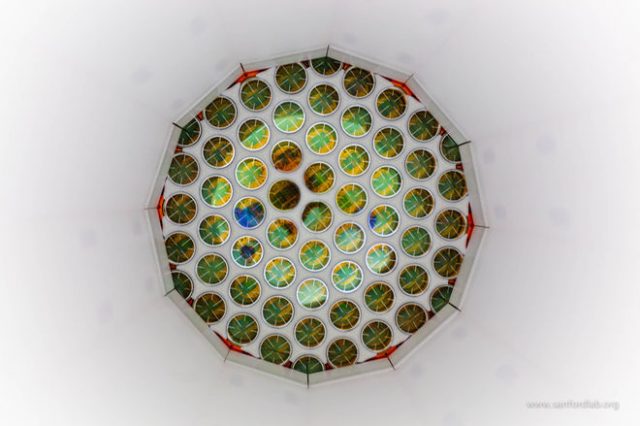
Ultra-sensitive detector fails to find sign of dark matter
The most sensitive search yet for dark matter has failed to turn up a signal from the elusive material believed to make up most of the universe’s mass, according to findings presented at the 11th Identification of Dark Matter Conference in the UK. The experiment pushed the Large Underground Xenon detector, or LUX, to new levels of sensitivity, researchers say, but it will now be replaced by an even more sensitive instrument, the LUX-Zeplin.
Nectar with more alcohol preferred choice of certain primates
Aye-ayes and slow lorises appear to prefer nectar with higher alcohol content. Researchers say the primates consistently chose the more fermented nectar in the small study that followed two aye-ayes and one slow loris over 30 trials.
Drought has affected Amazon’s ability to process carbon dioxide
A 2010 drought in the Amazon Basin has reduced the key area’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The drought resulted in the death of trees and slowed growth rates of surviving trees, affecting the Amazon’s role in processing carbon dioxide.
Gold-titanium alloy may create stronger, longer-lasting implants
Mixing gold and titanium has created a super-hard metal that could be used to make medical implants that last longer than current models. The new alloy, called beta-Ti3Au, is much harder than titanium and is also biocompatible, making it the “next generation compound for substantively extending the lifetime of dental implants and replacement joints,” said study author Emilia Morosan.
Infectious diseases spread by ancient Silk Road travelers
Infectious diseases were spread by travelers as they made their way along China’s Silk Road. Researchers found evidence of disease in feces recovered from a 2,000-year-old latrine along the ancient trade route network.