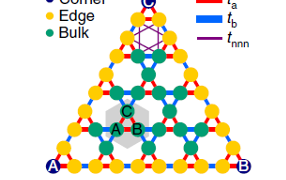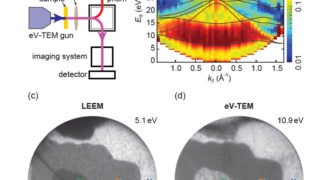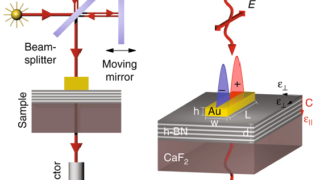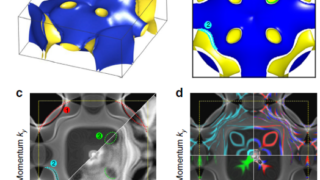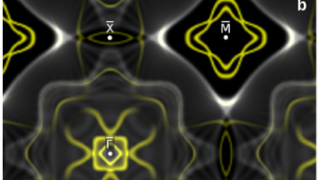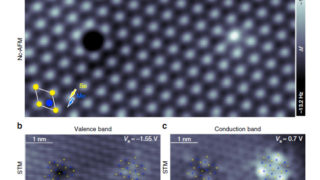
How to identify a point defect in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
A crystal lattice is formed by a repeated arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules. Due to the enormous amount of atoms involved it is extremely unlikely that all these will be arranged in perfect order. Some atoms will not be exactly in the right place with the result that the lattice will contain defects. The […]