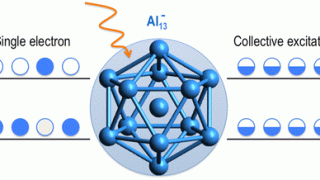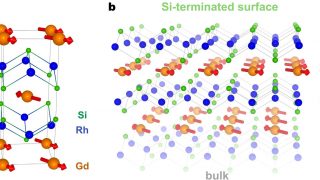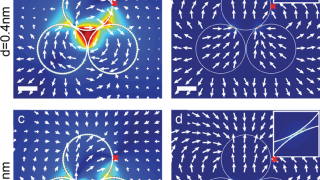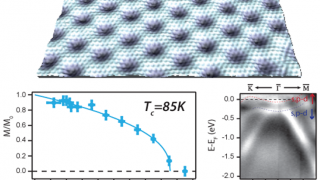
An ideal candidate to investigate nanoscale ferromagnets and exotic interfaces
In order to study new solid state magnetic properties appropiate new laboratory models are needed. In particular, there is a necessity for a substrate to investigate new forms of magnetic coupling with nanoscale ferromagnets and the exotic physics at the interface with semiconductor or superconductor materials. Now a team of researchers from DIPC and some […]