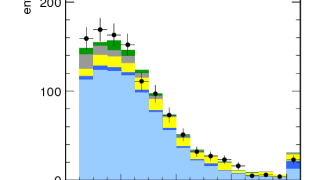
Evidence of brand new physics at Cern? Why we’re cautiously optimistic about our new findings
When Cern’s gargantuan accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), fired up ten years ago, hopes abounded that new particles would soon be discovered that could help us unravel physics’ deepest mysteries. Dark matter, microscopic black holes and hidden dimensions were just some of the possibilities. But aside from the spectacular discovery of the Higgs boson […]