Real-time imaging of the forces that build chemical gardens
Chemistry • DIPC Biochemistry • Evolution • Geosciences • Materials
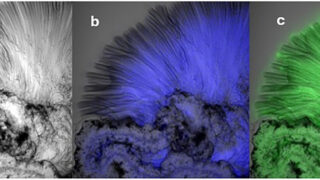
The classic chemical garden experiment is a staple of introductory chemistry, where colorful, plant-like structures sprout from metal salt crystals dropped into a solution of sodium silicate. While these vibrant tubes look like biological life, they are entirely inorganic, driven by the physics of osmosis and the chemistry of precipitation. For decades, scientists have admired […]