MI weekly selection #318
MI weekly selection #318
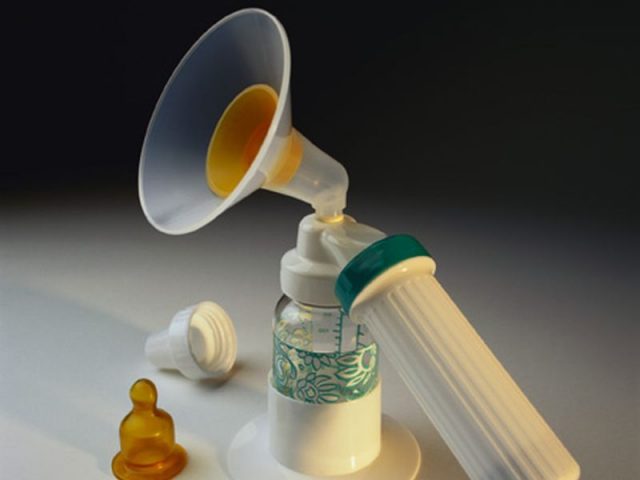
Mode of delivery may affect breast milk’s bacterial composition
Canadian researchers found that pumped breast milk had reduced levels of healthy bifidobacteria and elevated levels of some infection-causing bacteria, such as Pseudomonadaceae and Stenotrophomonas, compared with directly breastfed milk.
Honeybees’ brains tracked while navigating VR maze
Researchers got a glimpse into honeybee brains as the insects completed a maze in virtual reality. Electrodes were implanted in the bees’ front antennal lobes, allowing scientists to monitor their brains’ electrical activity as they moved through the virtual environment.
Toxin in gut bacteria causes damage to DNA
A toxin produced by certain strains of Escherichia coli can cause damaging changes to the DNA of gut cells, possibly leading to bowel cancer. Researchers injected the colibactin-producing E. coli into gastrointestinal cells and found that it caused DNA damage within minutes, but they say further investigation is needed to determine if this does lead to the development of cancer.
Gesturing chimpanzees use rules similar to human communication
Chimpanzees’ gestural communication follows rules much like those of human language, with the most commonly used gestures taking a shorter amount of time and longer sequences being broken up into shorter gestures. “Primate gestural communication is, of course, very different to human language, but our results show that these two systems are underpinned by the same mathematical principles,” said study co-author Raphaela Heesen.
Saliva-based test developed to detect malaria
A rapid, mobile test for malaria that uses saliva instead of blood has been developed to detect the disease in asymptomatic people. The test looks for the presence of a protein produced by the parasite that causes malaria.