Galaxies from the early Universe are more like our own Milky Way than previously thought
Galaxies from the early Universe are more like our own Milky Way than previously thought, flipping the entire narrative of how scientists think about structure formation in the Universe.
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of researchers has discovered 1 that galaxies like our own Milky Way dominate throughout the universe and are surprisingly common.
These galaxies go far back in the Universe’s history, with many of these galaxies forming 10 billion years ago or longer.
The Milky Way is a typical ‘disk’ galaxy, which a shape similar to a pancake or compact disk, rotating about its centre and often containing spiral arms. These galaxies are thought to be the most common in the nearby Universe and might be the types of galaxies where life can develop given the nature of their formation history.
However, astronomers previously considered that these types of galaxies were too fragile to exist in the early Universe when galaxy mergers were more common, destroying what we thought were their delicate shapes.
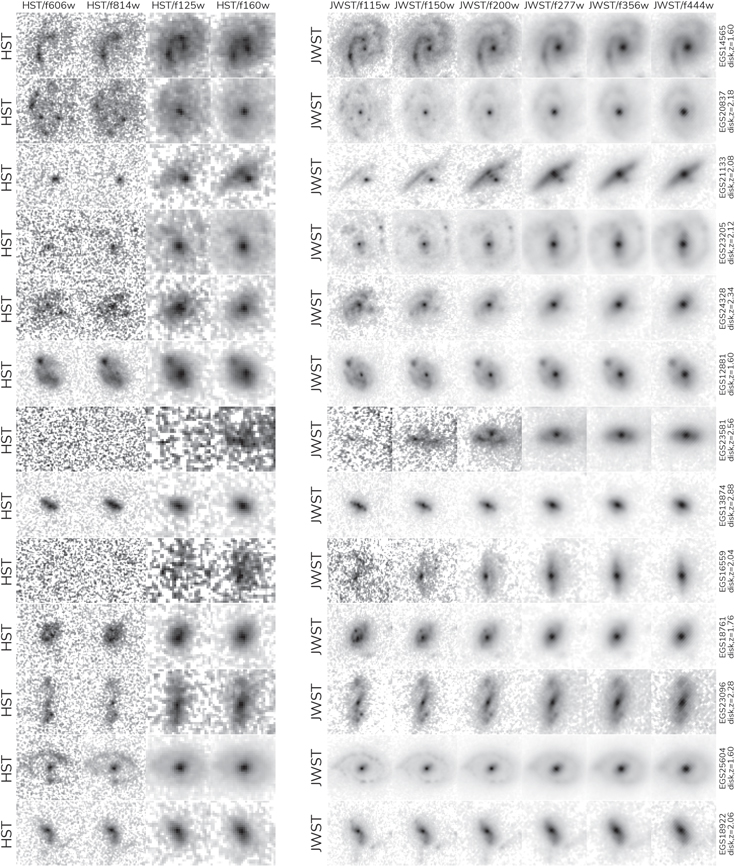
The new discovery finds that these ‘disk’ galaxies are ten times more common than what astronomers believed based on previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Using HST, disk galaxies were thought to be almost non-existent until the Universe was about six billion years old, these new JWST results push the time these Milky Way-like galaxies form to almost the beginning of the Universe.
The research completely overturns the existing understanding of how scientists think our Universe evolves, and the scientists say new ideas need to be considered.
For over 30 years it was thought that these disk galaxies were rare in the early Universe due to the common violent encounters that galaxies undergo. The fact that JWST finds so many is another sign of the power of this instrument and that the structures of galaxies form earlier in the Universe, much earlier in fact, than anyone had anticipated.
It was once thought that disk galaxies such as the Milky Way were relatively rare through cosmic history, and that they only formed after the Universe was already middle aged.
Previously, astronomers using HST believed that galaxies had mostly irregular and peculiar structures that resemble mergers. However, the superior abilities of JWST now allows us to see the true structure of these galaxies for the first time (see image for a comparison).
These JWST results show that disk galaxies, like our own Milky Way, are the most common type of galaxy in the Universe. This implies that most stars exist and form within these galaxies which is changing our complete understanding of how galaxy formation occurs. These results also suggest important questions about dark matter in the early Universe which we know very little about.
Based on these results astronomers must rethink our understanding of the formation of the first galaxies and how galaxy evolution occurred over the past 10 billion years.
References
- L. Ferreira et al. (2023) The JWST Hubble Sequence: The Rest-frame Optical Evolution of Galaxy Structure at 1.5 < z < 6.5 The Astrophysical Journal doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/acec76 ↩