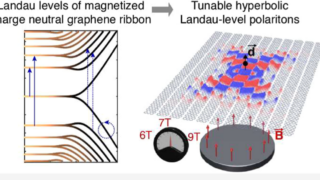
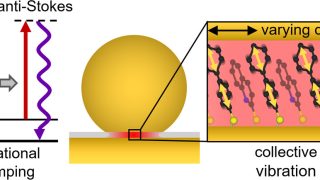
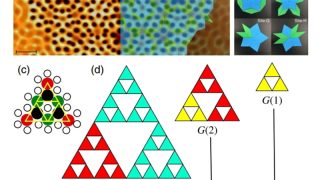
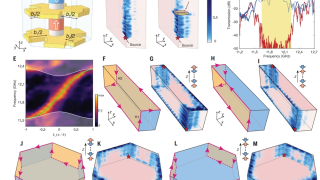
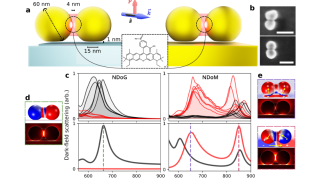
The surprising memory of Stokes-shifted photons
In recent decades, researchers have developed advanced techniques to detect and manipulate individual photons. A particularly intriguing field examines how nanoscale light emitters, resembling artificial atoms, produce these photons. In this vein, a new study addresses a subtle question: when two such emitters release photons that are red-shifted due to energy loss, do these photons […]