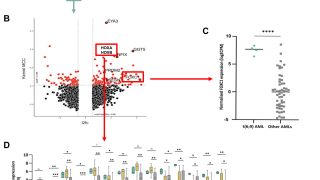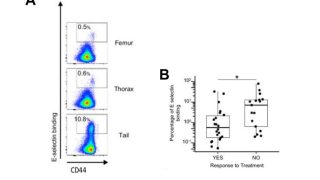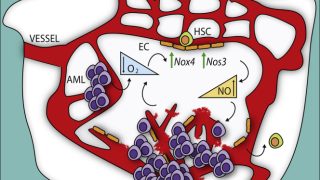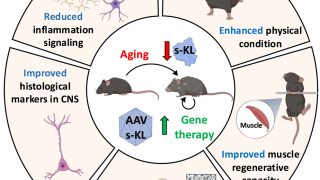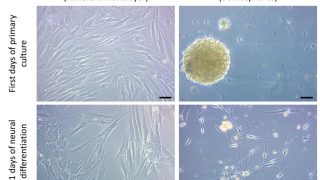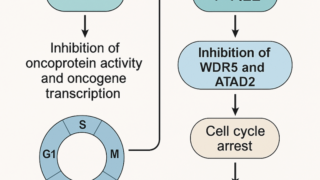
Targeting WDR5/ATAD2 signaling by the CK2/IKAROS axis demonstrates therapeutic efficacy in T-ALL
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy with a poor prognosis and limited options for targeted therapies . Since the targeted therapies benefiting T-ALL are still limited owing to the biological heterogeneity of T-ALL , identifying novel “druggable” molecular markers and illustrating the underlying mechanisms are immediate pressing issues in T-ALL […]