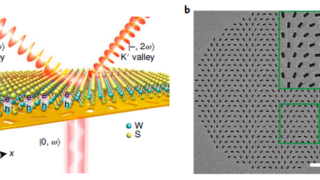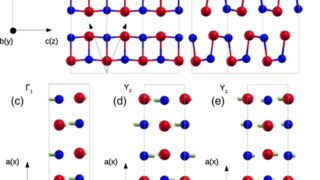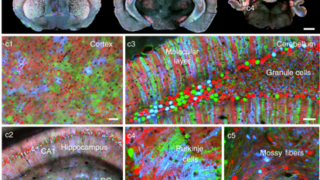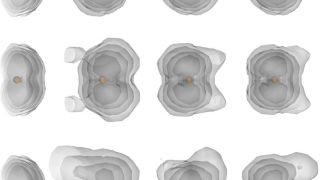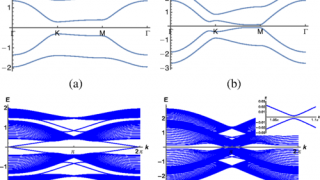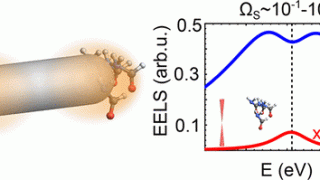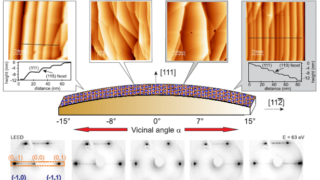
Hexagonal boron nitride monolayer films can be successfully grown on a curved Ni(1 1 1) substrate
Since the discovery of graphene, a wide diversity of atomic-layer-thick, two-dimensional (2D) materials with varied properties have emerged. Of particular interest are those that exhibit semiconducting behavior, such as hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). hBN is isoelectronic to graphene and has also a honeycomb lattice formed by alternating nitrogen and boron atoms, but in contrast to […]