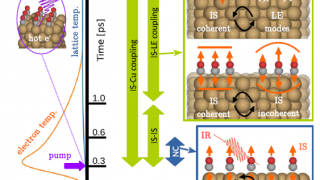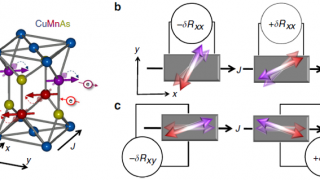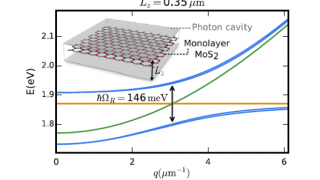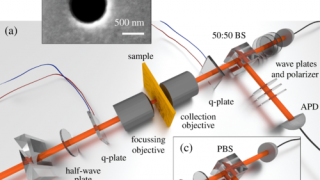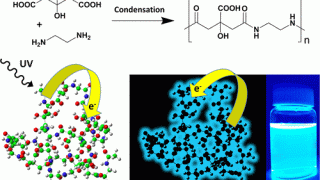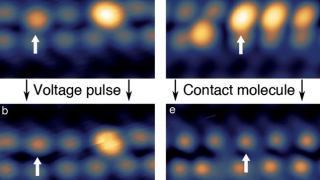
Spin in a closed-shell organic molecule stabilized on a metallic surface
Chemistry • Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Quantum physics
Every year the amount of data produced is of the order of magnitude of the Avogadro’s constant, thus 6.028×1023. This trend is supposed to increase even more in the next future. This implies that more and more special metals will be needed. The point is: what might happen if the resources used for manufacturing common […]