Quantum and relativistic effects unified in electron spin-lattice interactions
Quantum and relativistic effects unified in electron spin-lattice interactions
“God does not play dice.” This famous remark by Albert Einstein critiqued the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics. Paradoxically, his theory of relativity has become an essential tool for understanding the behaviour of electrons, the primary subjects of quantum mechanics. Electrons are so minuscule that their behaviour must be analysed through quantum mechanics, yet they also move at speeds that require relativistic considerations. Due to the fundamentally different starting points of these two theories, achieving a unified, consistent description has posed significant challenges.
Now, a groundbreaking study 1 offers a novel approach that bridges this divide, potentially reshaping the way we understand electron dynamics in solids.
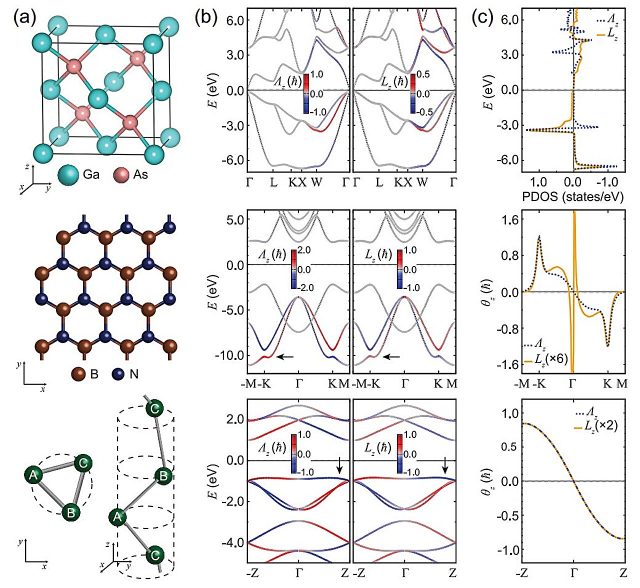
A team of researchers led by Professor Noejung Park in the Department of Physics at UNIST and Professor Kyoung-Whan Kim of Yonsei University has introduced a new theoretical framework that enables more accurate descriptions of electron spin within solid materials.
Electrons possess two types of angular momentum: spin and orbital angular momentum. To draw an analogy, spin can be likened to Earth’s rotation, while orbital angular momentum resembles Earth’s revolution around the sun.
These two forms of angular momentum influence each other through spin-orbit coupling, which plays a vital role in determining a material’s magnetic and conductive properties.
However, the spin-orbit interaction arises predominantly from relativistic effects at high energies, whereas in solid-state systems such as semiconductors, quantum mechanical phenomena at low energies dominate.
References
- Kim, Bumseop, Park, Noejung and Kim, Kyoung-Whan (2025) Relativistic Spin-Lattice Interaction Compatible with Discrete Translation Symmetry in Solids Phys. Rev. Lett. doi: 10.1103/q46t-hck1 ↩