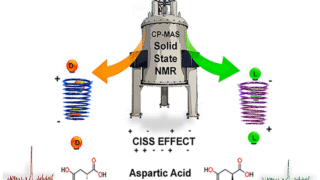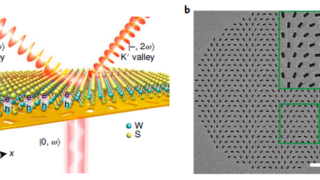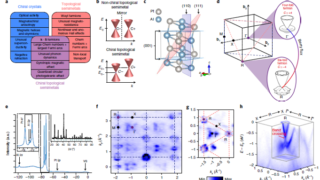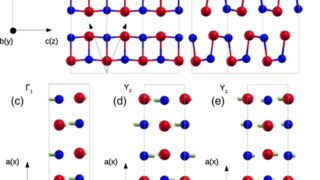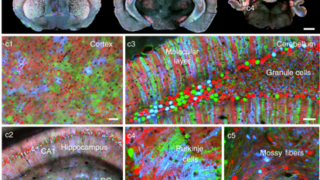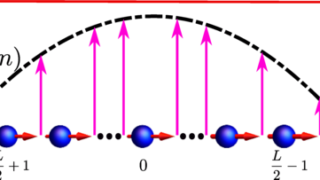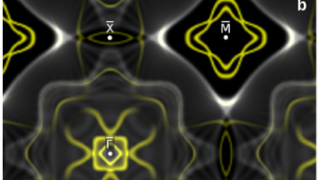
Non-magnetic in the bulk, strongly ferromagnetic at the surface
For a successful application in spintronics of any material, a key problem is to get a reliable control of the electronic spin within it. An ideal candidate for this purpose would be any material which is non-magnetic in the bulk but has a tunable ferromagnetic surface layer with a large splitting of the spin-up and […]