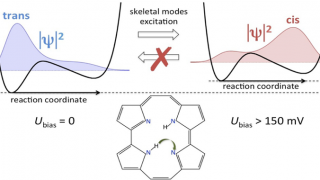
The tautomerization of porphycene on Cu(111) in simple physical terms
There are compounds, called isomers, that have the same molecular formulae but different molecular structures or different arrangements of atoms in space. In the so-called cis-trans isomerism, isomers have different positions of groups or specific atoms with respect to a double bond, a ring or a central atom. For example, the numbers in the name […]