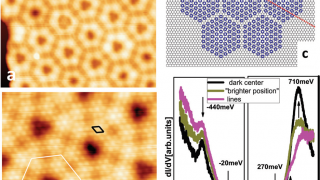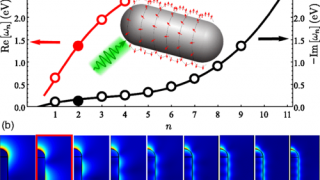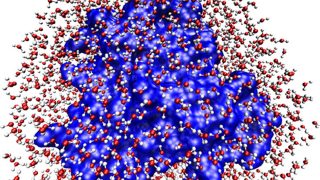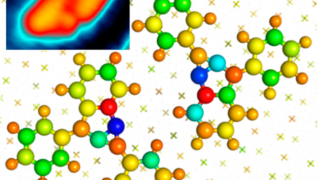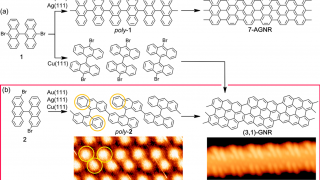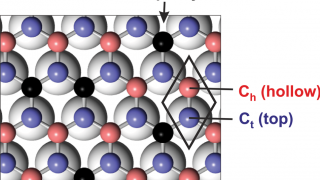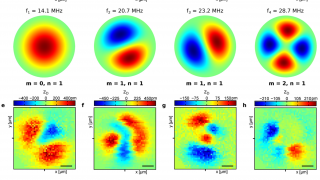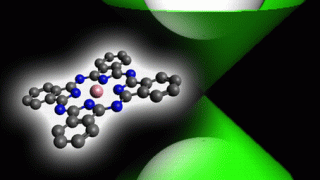
Manipulating the topological surface states with molecular adsorbates
A topological insulator is a material in which there is order associated to topology, i.e., the surface can conduct electricity but the bulk of the material is an insulator. In these last years topological insulators have received the attention of a large area of the scientific community thanks to their exotic properties. They are promising […]