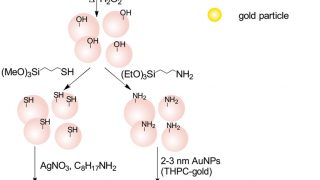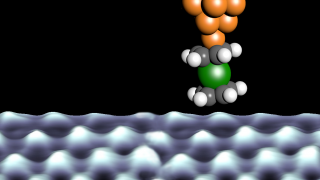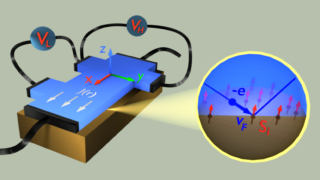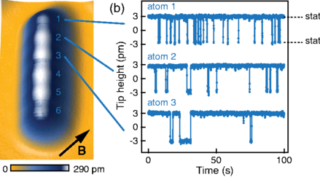
First ever antiferromagnetic topological insulator discovered
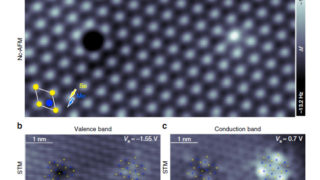
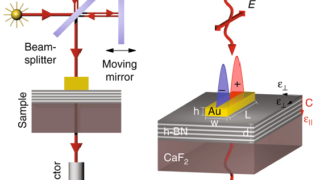
Topological insulators are materials with special universal properties, which are protected against perturbations. Such properties are theoretically described by topology, a branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of geometrical objects that are unchanged by continuous deformations. Topological insulators are electronic materials that have a bulk band gap like an ordinary insulator but have conducting […]