MI weekly Selection #192
MI weekly Selection #192
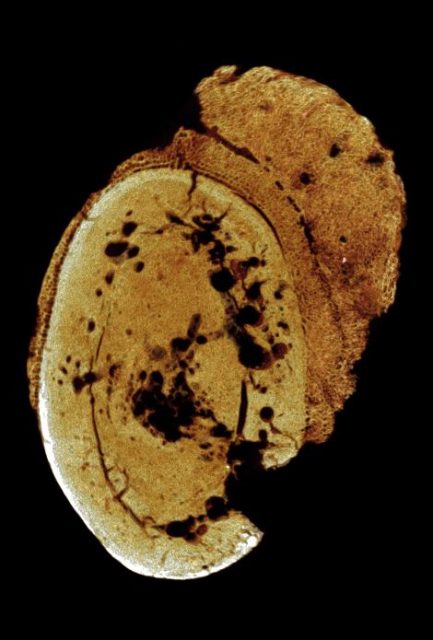
Cancer found in bone of ancient human ancestor
Evidence of cancer has been found in the toe bone of an ancient human ancestor who died 1.6 million to 1.8 million years ago, suggesting the deadly disease isn’t just caused by lifestyle factors. Researchers examining the bone using 3D imaging identified a malignant osteosarcoma tumor.
Distinguishing gray wolf from hybrid species
The gray wolf is the only true species of wolf in North America, and the rest are hybrids of the gray wolf and coyotes. The findings may help gray wolves continue to receive protection under the Endangered Species Act.
Ancient rice crops more diverse than previously thought
Many different kinds of rice were farmed in Asia between 950 and 2,800 years ago, according to DNA analysis findings. Researchers examined the genomes of rice grains found at archaeological sites in Japan and Korea and were surprised at the diversity, which suggests the grain may have traveled more widely than previously thought.
Distant binary star system gives off pulses of light
A distant binary star system pulses brightly every couple of minutes. The white dwarf star in the AR Scorpii system smacks its larger red dwarf companion with a beam of radiation as the white dwarf swiftly spins and revs up electrons close to it, causing the whole system to glow brighter every time the beam hits the red dwarf.
Nose-dwelling bacteria produces strong potential antibiotic
An antibiotic compound created by a bacteria that resides in human noses has the potential to destroy a number of pathogens, including MRSA. The antibiotic compound, dubbed lugdunin, has been tested in mice, treating a skin infection.