MI weekly selection #390
Mouse mom’s microbiome may affect her young
A mouse mother’s gut microbes may play an important role in offspring’s brain development, according to findings published in Nature. Particular gut microbes produce metabolites that travel to the fetuses’ brains, affecting the growth of axons, which act as nerve cell signal transmitters.
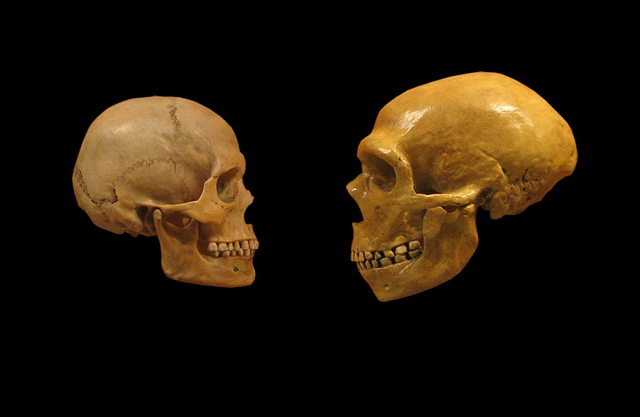
Homo sapiens Y chromosome found in Neanderthal DNA
A new sequencing method has allowed researchers to find human-like Y chromosomes in Neanderthal DNA and the process is described in Science. Researchers estimate the Homo sapiens version of the Y chromosome took over the Neanderthal chromosome between 370,000 and 100,000 years ago.
New kind of superconductor discovered
Physicists discovered a g-wave superconductor while analysing strontium ruthenate during a resonant ultrasound spectroscopy. The g-wave superconductor exhibits an angular momentum not seen in s-wave or d-wave superconductors.
Arctic sea ice declines to near-record low
Scientists who monitor Arctic sea ice report that it has hit the second-lowest level on record this year. Only 3.74 million square kilometres of Arctic waters were covered with ice as of Sept. 15, marking the second time in a span of more than 40 years of satellite measurements that yearly minimum coverage has fallen below 4 million square kilometres, according to figures from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center.
Rates of COVID-19 vary by race, ethnicity
A study in PLOS Medicine showed Black and Hispanic people were more than two times more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than white people, even after accounting for type of residence, site of care and underlying health conditions. The research, based on health records from over 5.8 million Veterans Affairs patients, did not find any difference in 30-day mortality among the groups.