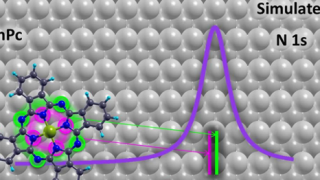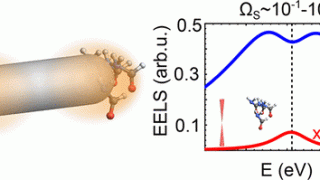
Surface-Enhanced Molecular Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy
Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Physics • Quantum physics • Theoretical physics
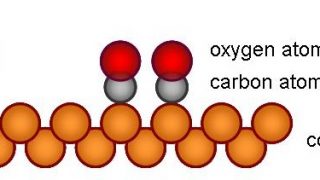
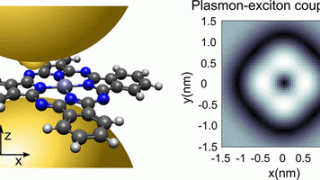
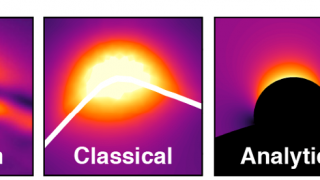
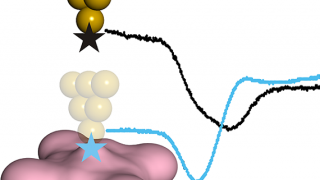
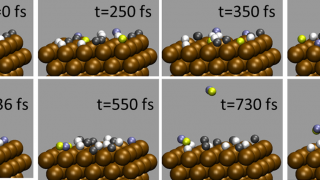
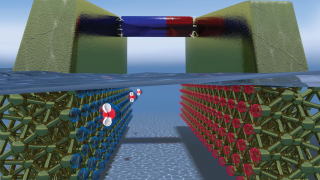
Chemists have a range of different spectroscopic techniques to study organic molecules. All of these techniques are based on spectra generated by a range of electronic transitions and vibrations, key excitations in matter, the study of which provides information about characteristics of materials and, therefore, allow their identification. In this context, one of those spectroscopic […]