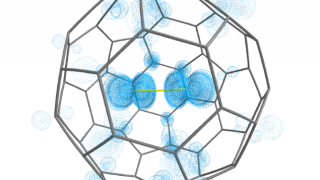
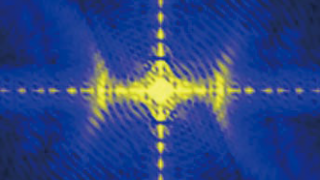
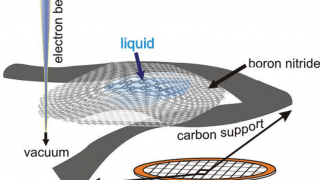
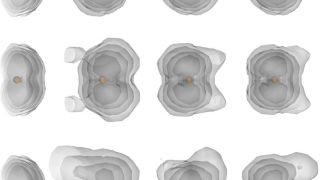
Nonequilibrium effects in hybrids of electron systems with spontaneously broken symmetries
Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Quantum physics
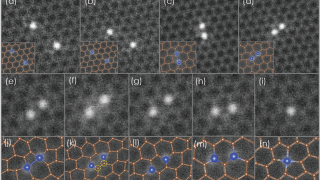
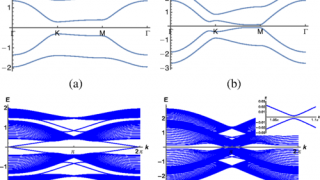
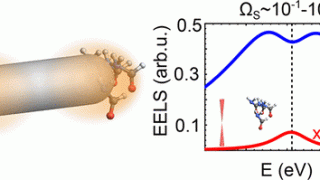
Imagine a military regiment in formation. That we will call symmetry. Now imagine the same regiment when it is dismissed by the commanding officer: at once the soldiers disperse and tend to form domains (groups) or pairs. Hence, we can say that the symmetry is spontaneously broken. Both superconductors and ferromagnets are examples of electron […]