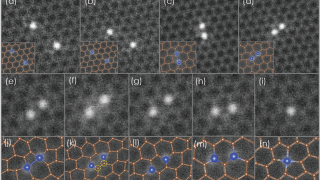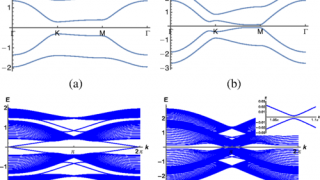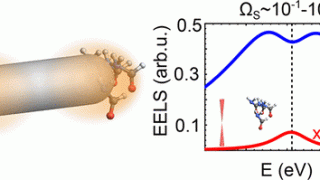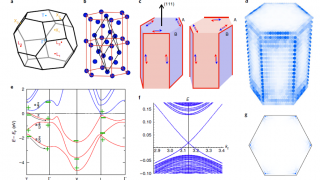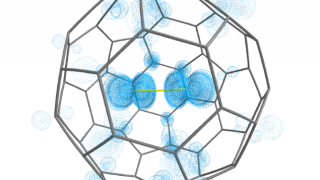
Buckyball difluoride, a single-molecule crystal
Endohedral fullerenes, also called endofullerenes, are fullerenes that have additional atoms, ions, or clusters enclosed within their inner spheres. The first lanthanum C60 complex was synthesized in 1985 and called La@C60. The @ (at sign) in the name reflects the notion of a small molecule trapped inside a shell. The chemistry of endohedral fullerenes is […]