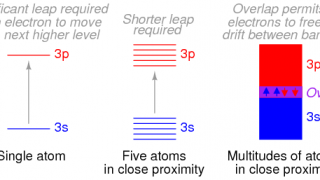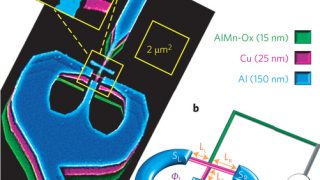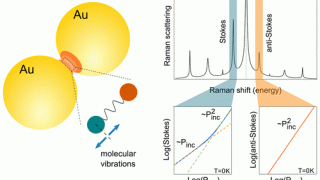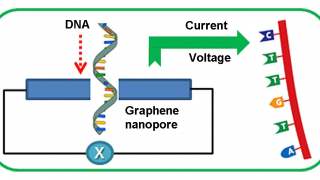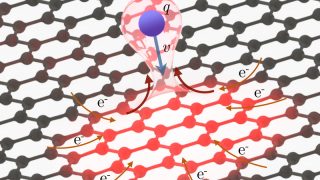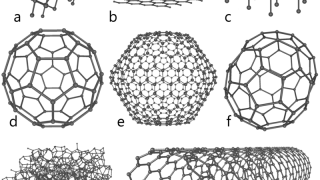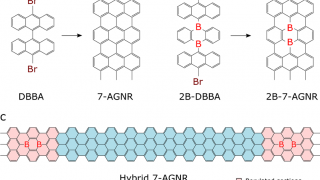
Quantum dots embedded in graphene nanoribbons
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), are strips of graphene with ultra-thin width (<50 nm). Graphene ribbons were introduced as a theoretical model by Mitsutaka Fujita and coauthors to examine the edge and nanoscale size effect in graphene. GNRs are very interesting structures, partly due to their attractive electronic properties. Those properties vary dramatically with changes in the […]