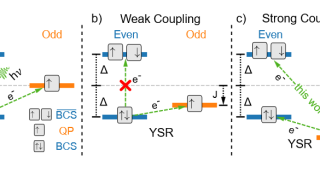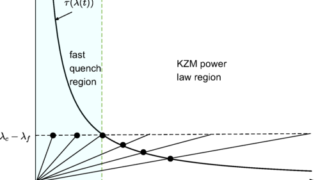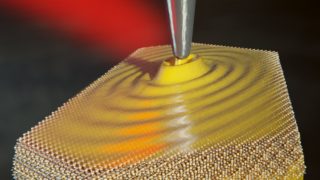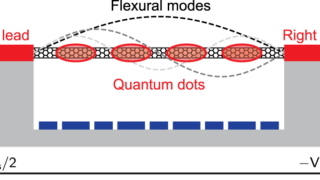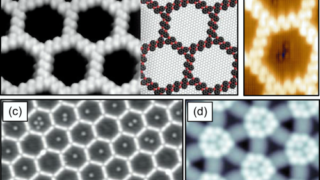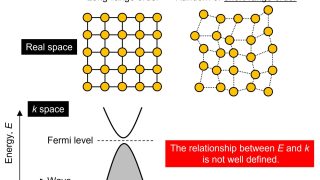
A topological amorphous alloy
amorphous Scientists have dedicated their efforts to studying topological materials, focusing on the shape, or topology, of their electronic structures. These materials exhibit unique properties that have the potential to be harnessed for next-generation devices, despite their invisible nature in real space. Initially, it was believed that only crystalline materials, characterized by highly ordered atoms […]