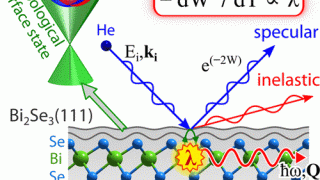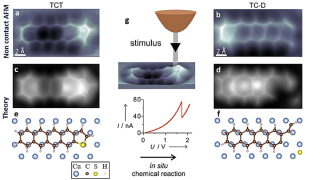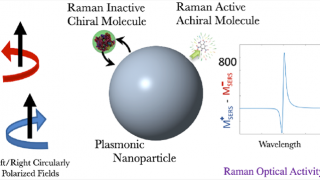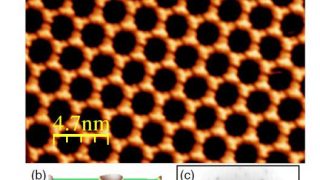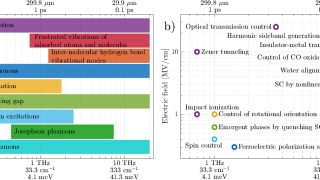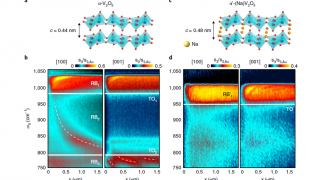
On-demand spectral response of phonon polaritons in van der Waals materials
In the quantum theory of many-body systems, collective oscillations are called collective excitations. In a quantum context, everything is quantized. Hence, collective excitations become quantized modes because of the cooperative motion of the whole system as a result of interactions between particles. They may be electronic excitations in atoms and are referred excitons. In most […]