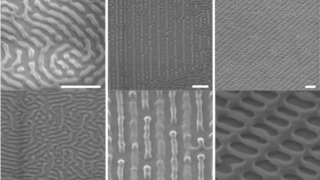
Sharp separation using isoporous membranes
Chemical engineering • Food processing • Materials • Mechanical Engineering • Nanotechnology
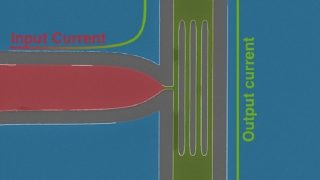
Imagine a close basketball game that comes down to the final shot. The probability of the ball going through the hoop might be fairly low, but it would dramatically increase if the player were afforded the opportunity to shoot it over and over. A similar idea is at play in the scientific field of membrane […]