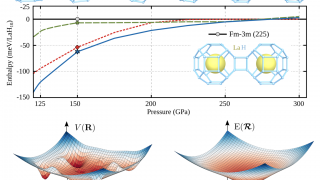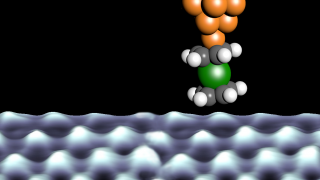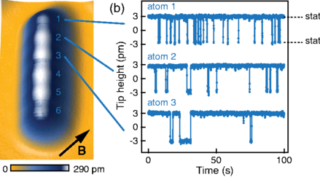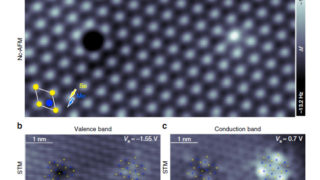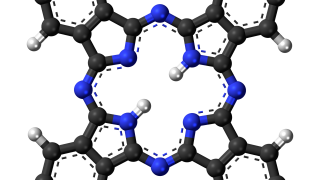
Tracking the tautomerization of a single molecule in space and time
There are chemical compounds, called isomers, that have the same molecular formulae but different molecular structures or different arrangements of atoms in space. In constitutional isomerism the molecules have different molecular structures: i.e., they may be different types of compound, or they may simply differ in the position of the functional group in the molecule […]