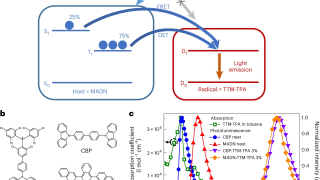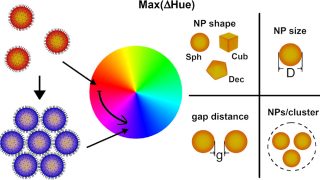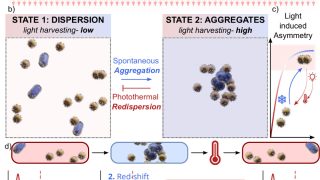
Oscillatory hydrodynamics in DNA-coated gold nanoparticles
Periodic responses to nonperiodic energy inputs, such as oscillations, are hallmarks of living systems. Researchers have devoted considerable efforts to understanding and mimicking natural self-assembled structures and functions to systems composed of nonbiological components. This has rendered remarkable developments in regulating interparticle interactions to form static and dynamic self-assemblies. Dynamic assemblies can, under suitable stimuli […]