Metal substrates in catalytic reactions
Catalysis • Chemistry • DIPC Biochemistry • DIPC Photochemistry
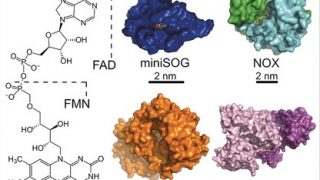
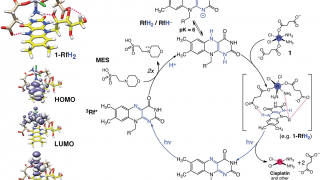
When we consider the concepts metal and catalysis, we tend to assume quite matter-of-factly that the metal will be the catalyst. This assumption is based on the fact that metals can be found in reactions where they act as catalysts or co-catalysts in the form of coordination and organometallic compounds, nano-sized or bulk materials and […]