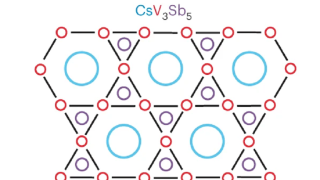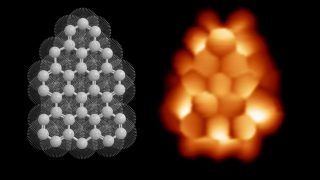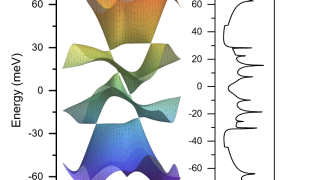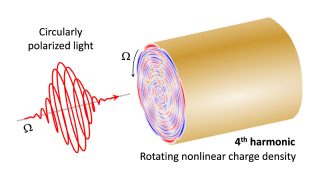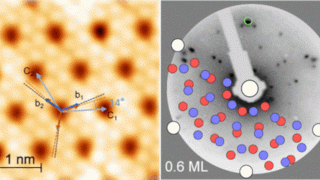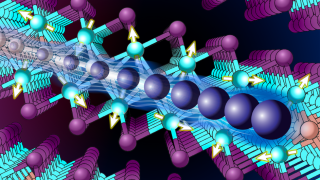
Heavy fermions in a 2D van der Waals metal
A team of researchers has successfully synthesized the first 2D heavy fermion material. The new material is a layered intermetallic crystal composed of cerium, silicon, and iodine (CeSiI) . Heavy fermion compounds are a class of materials with electrons that are up to 1000x heavier than usual. In these materials, electrons get tangled up with […]