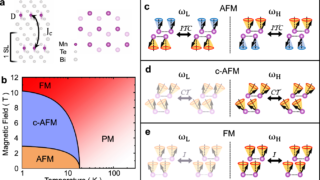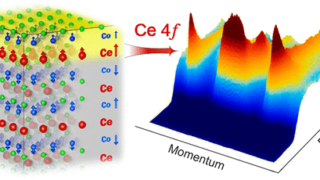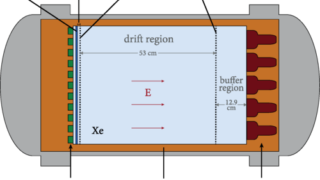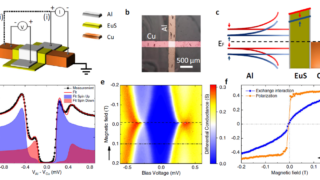
A general procedure to design materials with topological semimetal phases
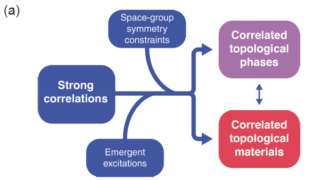
Electron correlations and topology are well established as engines for surprising and potentially functional properties. Strong correlations promote quantum fluctuations, which engender abundant phases of matter and various quantum phase transitions. Meanwhile, extensive developments have taken place in noninteracting electron systems, especially those with sizable spin-orbit couplings. It can reasonably be expected that the intersection […]