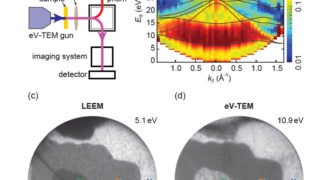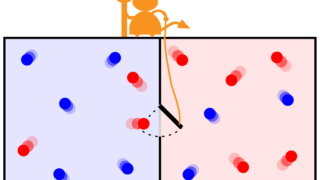
Maxwell’s demon and the relationship between information and irreversibility
Thermodynamics is one of the oldest physical theories with its origins going back to the beginnings of the 19th century. The theory was initially developed to tackle practical problems, such as the performance of steam engines. However, within a few decades, thermodynamics was formulated on firm grounds providing one of the most fundamental laws of […]