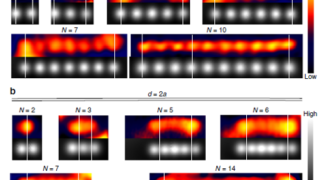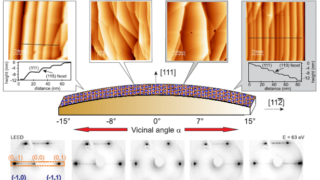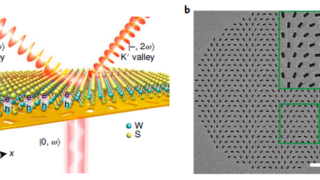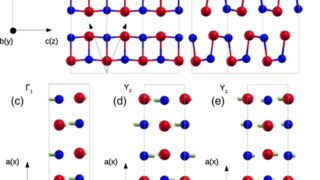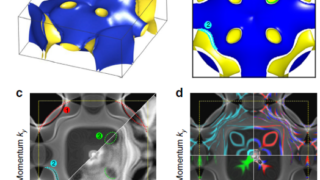
First direct visualization by photoemision of how the Luttinger theorem works for Kondo lattices
Elements with 4f or 5f electrons in unfilled electron bands and their componuds , which have ions carrying magnetic moments but do not magnetically order, or only do so at very low temperatures, are generally known as heavy-fermion or heavy electron systems because the scattering of the conduction electrons with the magnetic ions results in […]