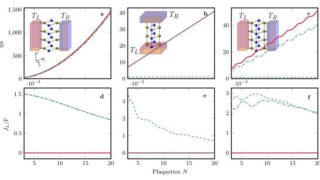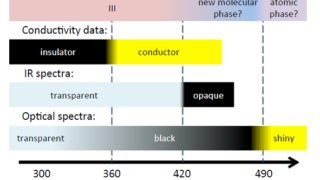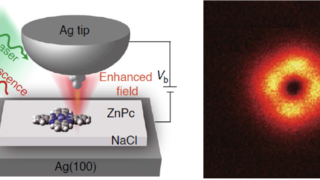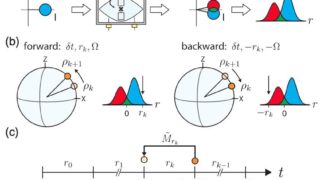
The essential physics of the Mott metal-insulator transition at negligible computational cost
DIPC Electronic Properties • Quantum physics • Theoretical physics
Density functional theory (DFT) is a theoretical treatment of molecules in which the electron density is considered rather than the wave functions of individual electrons. In other words, it is a way of describing many-electron, in general, many-fermion, systems in which the energy is a funtional of the density of electrons (fermions). DFT is without […]