The extreme nanophotonics of the plasmonic nanopatch
Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Quantum physics
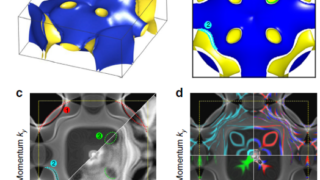
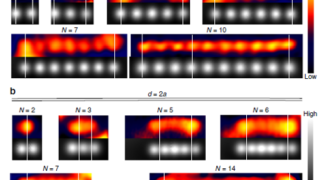
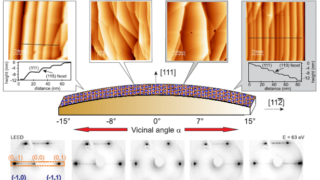
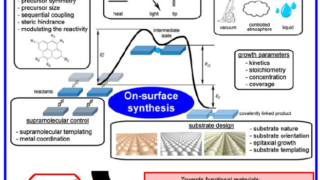
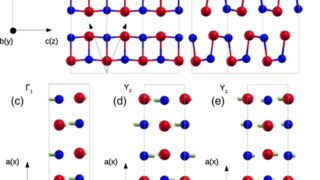
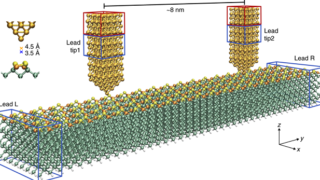
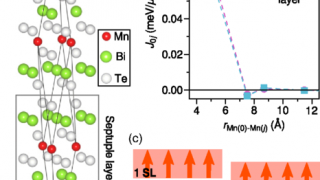
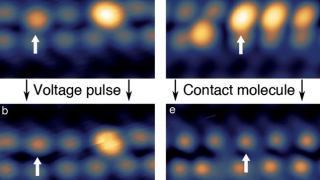
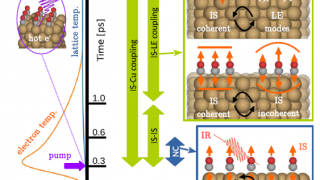
For centuries, metals were employed in optical applications only as mirrors and gratings. New vistas opened up in the late 1970s and early 1980s with the discovery of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and the use of surface plasmon (collective electronic oscillations at the surface of metals) resonances for sensing. In a simplified picture and in […]