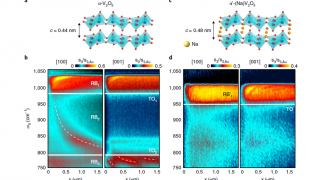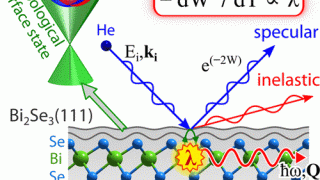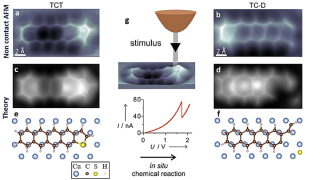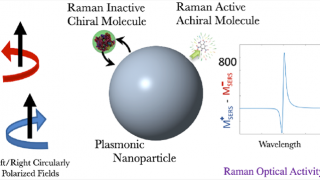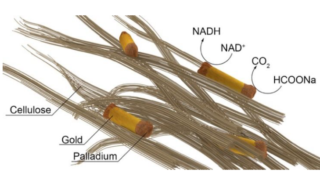
Plasmonic nanocrystals-cellulose hybrid
When we consider the variety of possible wonder applications of plasmonic nanoparticles we usually forget a key aspect: how these laboratory results can be transformed into something really usable in everyday life. For that to occur some not-that-simple problems must be resolved first. For example, plasmonic nanoparticles exhibit excellent light-harvesting properties in the visible spectral […]