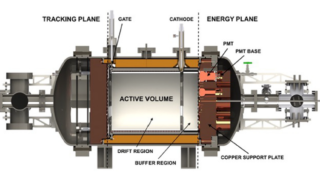
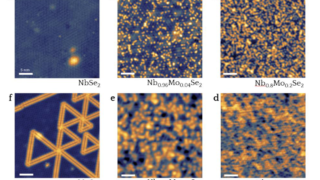
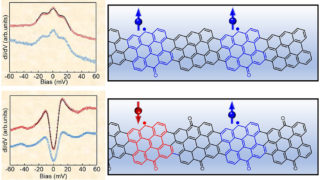
Topology for every electronic band
For the past century, students of chemistry, materials science, and physics have been taught to model solid-state materials by considering their chemical composition, the number and location of their electrons, and lastly, the role of more complicated interactions. However, an international team of scientists has recently discovered that an additional ingredient must also be equally […]